Understanding the traffic light sequence is crucial when you’re learning how to navigate the roads. While it’s common to focus on the less frequent road signs and symbols, it’s vital not to overlook the everyday ones, like traffic lights.
Traffic lights are more than just familiar street furniture; they’re key to managing traffic and preventing accidents. Knowing what each signal in the traffic light sequence means is essential, not just for your theory test but also for practical test.
This guide will walk you through the entire traffic light sequence, including the less common flashing amber lights. We’ll delve into the significance of green filter arrows and emphasise why it’s important to stop at red lights, even when an emergency vehicle is behind you.
What Are Traffic Lights For?
Purpose of Traffic Lights
Traffic lights are an essential component of road infrastructure, designed to regulate and manage the movement of vehicles and pedestrians.
The primary purpose of traffic lights is to ensure that road users can navigate intersections and crossings safely and efficiently.
By assigning the right of way to different streams of traffic, traffic lights help prevent accidents and promote orderly flow on the roads.
How They Control Traffic Flow
Traffic lights control traffic flow by using a system of coloured lights—red, amber, and green—to communicate with drivers and pedestrians.
Each colour conveys a specific instruction, guiding when it is safe to go, when to prepare to stop, and when stopping is mandatory.
This system is crucial for managing intersections where multiple roads converge, as it prevents conflicting movements that could lead to collisions.
Modern traffic lights often incorporate sensors and timers to adapt to real-time traffic conditions, enhancing their ability to manage traffic flow efficiently.
For example, during peak hours, the green light might stay on longer for busy directions to alleviate congestion.
Conversely, during off-peak hours, the lights can be timed to reduce unnecessary waiting.
Enhancing Road Safety
One of the primary roles of traffic lights is to enhance road safety. By clearly indicating who has the right of way, traffic lights reduce the likelihood of accidents at intersections.
The red light stops traffic completely, preventing potential collisions that can occur when drivers misjudge the intentions of other road users.
The amber light serves as a warning, giving drivers time to prepare to stop, which reduces abrupt braking and the risk of rear-end collisions.
Moreover, traffic lights contribute to road safety by managing pedestrian crossings.
Pedestrian signals, often integrated with traffic lights, provide safe intervals for pedestrians to cross roads, thereby reducing the risk of accidents involving pedestrians.
Reducing Congestion
Traffic lights play a crucial role in reducing traffic congestion. By regulating the flow of vehicles through intersections, they prevent bottlenecks that can lead to significant delays.
When properly timed, traffic lights can improve the overall efficiency of a road network, ensuring that traffic moves smoothly even during busy periods.
Advanced traffic light systems use data from sensors and cameras to adjust their timing dynamically.
This real-time adjustment helps manage varying traffic volumes, ensuring that congestion is minimised.
For instance, during peak hours, traffic lights may allow longer green phases for heavily travelled routes, while during lighter traffic periods, they can revert to shorter cycles.
Pedestrian Safety
Traffic lights significantly enhance pedestrian safety by providing controlled crossing points.
Pedestrian signals often work in conjunction with traffic lights, indicating when it is safe for pedestrians to cross the road.
These signals reduce the risk of pedestrians crossing at inappropriate times, which can lead to accidents.
In areas with high pedestrian traffic, traffic lights are crucial for managing the interaction between vehicles and pedestrians.
The clear indication of when to walk and when to wait helps protect pedestrians, particularly in busy urban environments.
Additionally, features such as audible signals for visually impaired individuals further enhance pedestrian safety.
Understanding the Traffic Light Sequence
Navigating through traffic lights is a fundamental skill for all drivers. Here’s a straightforward breakdown of the typical traffic light sequence and what each phase signifies:
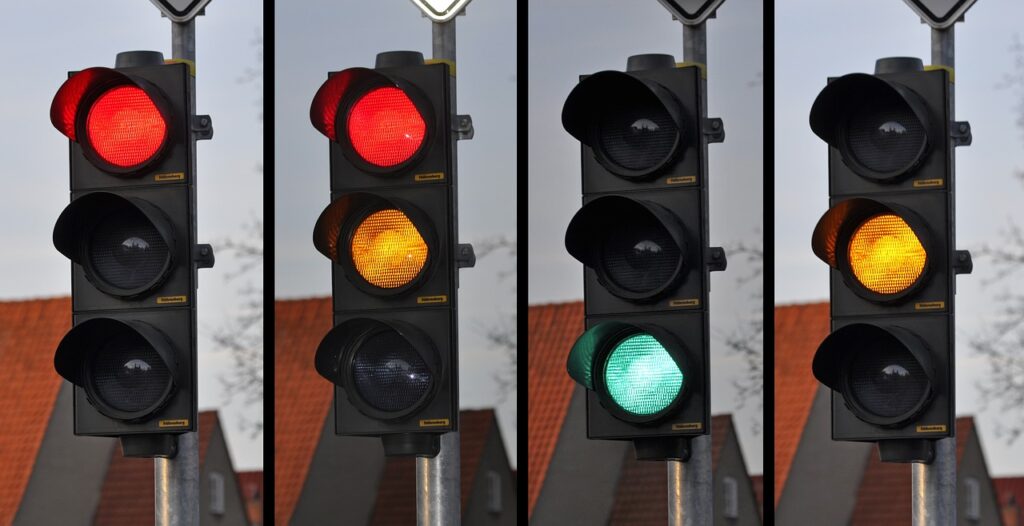

Image source: Wikimedia images
-
Red (Stop): This is a clear signal to halt your vehicle.
-
Red and Amber (Prepare to Pull Away): Get ready to move, but don’t start driving yet.
Or
Flashing Amber (Give Way to Pedestrians): Yield to pedestrians crossing the road. Proceed only when it’s safe.
-
Green (Go): This indicates it’s safe to drive on.
-
Amber (Stop unless It’s Not Safe to Do So): Prepare to stop, unless you’re too close to the lights to do so safely.
And then, the sequence repeats!
While this might sound straightforward, it’s crucial to fully understand these rules to ensure safe and confident driving.
Stopping at a Red Traffic Light
Understanding and adhering to traffic light rules is a fundamental aspect of safe driving. Here’s an in-depth look at what to do when you encounter a red light:
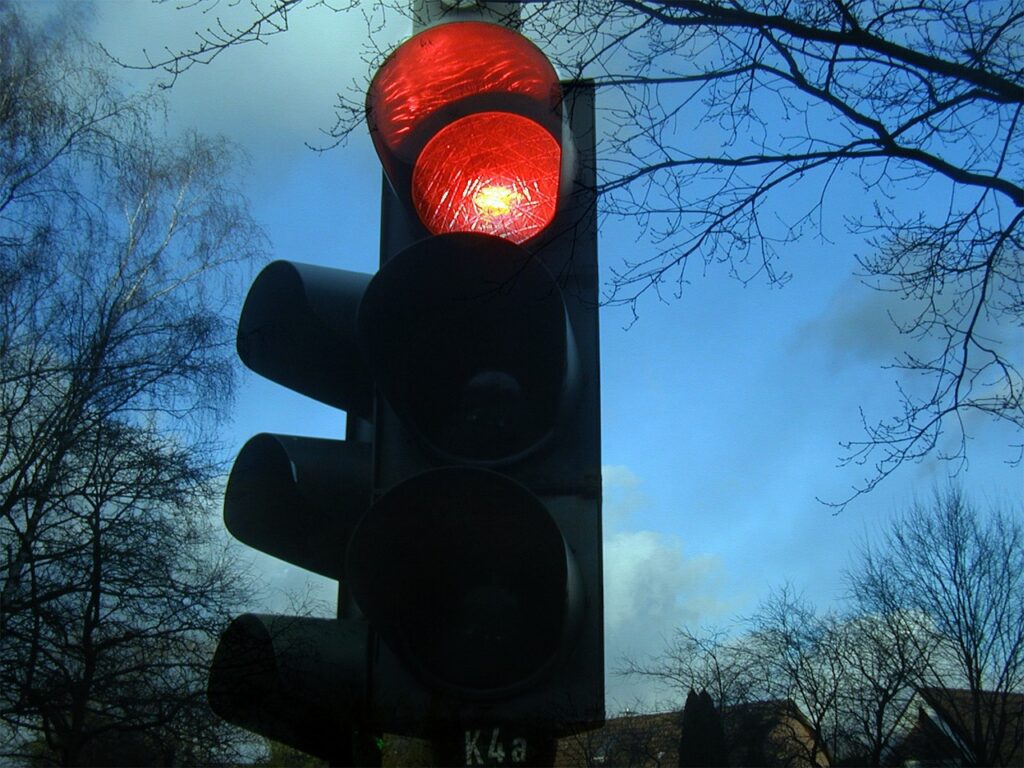

Image source: kalhh
-
Red Means Stop: The red traffic light is a non-negotiable instruction to stop your vehicle. Driving through a red light is not only dangerous but also a legal offence. It can lead to fines and points on your license. Traffic cameras are often installed at junctions to enforce this rule.
-
Correct Stopping Procedure: When you see a red light:
- Check your mirrors.
- Slow down gradually and smoothly.
- Stop behind the vehicle in front, leaving a safe distance.
- Engage the handbrake.
- Shift to neutral.
- Relax your feet off the pedals to prevent rolling or stalling.
-
Stay Alert and Undistracted: While waiting at a red light, remain vigilant. Avoid distractions such as using your phone or applying makeup, as these activities are not only unsafe but also illegal when behind the wheel.
Where to Stop at a Red Light?
- The Solid White Line: This line indicates where your vehicle must stop at a red light. Ensure no part of your vehicle crosses this line.
- Consider Cyclists: Often, there’s a designated area in front of the white line for cyclists. Keep this space clear to enhance their safety. Giving cyclists priority positioning at junctions helps protect these vulnerable road users.
Key Points to Remember:
- Always halt your vehicle behind the solid white line at a red traffic light.
- Apply your handbrake and shift to neutral.
- Avoid any distractions while stopped, such as using your phone or other activities that take your focus off the road.
Red and Amber Traffic Lights
When faced with red and amber lights at a traffic junction, it’s essential to understand and follow the correct procedure:
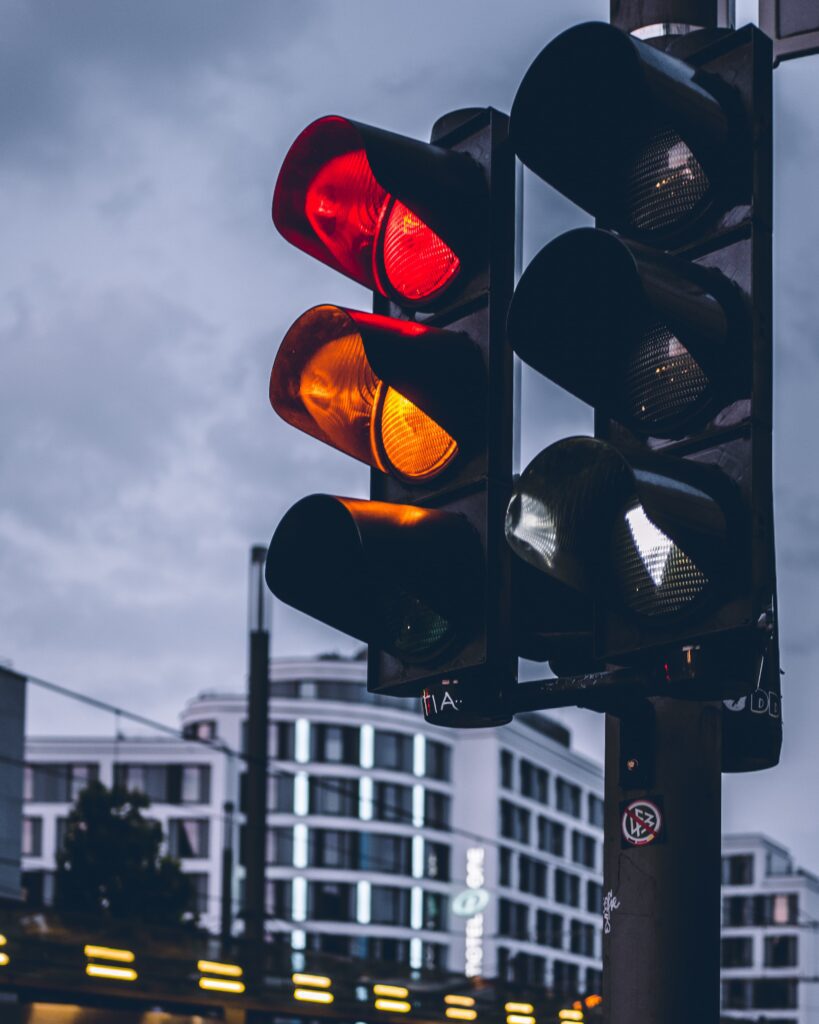

Image source: Maxim Abramov
-
Red and Amber Together Means ‘Prepare to Go’: This combination signals that green is imminent, but it’s crucial to remember that the red light is still active, which means stop. At this stage, you should not move your vehicle forward or cross the solid white line on the road. Moving early can create hazards for other road users, including pedestrians and cyclists.
-
Preparing for Green:
- Gear Up: Get ready for the green light by engaging the appropriate gear in anticipation of moving off.
- Observation Checks: Perform thorough checks by looking in all three mirrors. Pay special attention to any cyclists or pedestrians at the junction.
- Handbrake and Clutch Control: Keep your handbrake engaged to ensure your car remains stationary. Gradually release the clutch to find the biting point, so you’re ready to move off smoothly when the light turns green.
Additional Points to Remember:
- Avoid creeping forward when the lights are red and amber. Stay behind the solid white line.
- Regularly check your mirrors for a full awareness of your surroundings.
- Select the appropriate gear and be ready to move off as soon as the light turns green, ensuring a swift and safe departure from the junction.
Flashing Amber Traffic Lights
Understanding the specific rules for flashing amber traffic lights, especially at pedestrian crossings like pelican crossings, is crucial for safe driving:
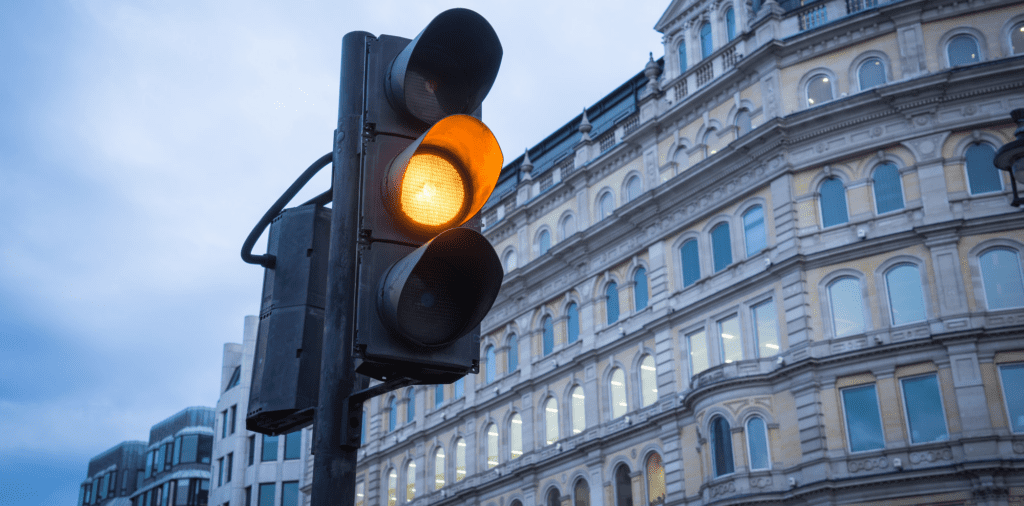

-
Pelican Crossings and Flashing Amber: At pelican crossings (marked with red and green figures), the traffic lights have a unique sequence. Instead of changing to red and amber, they flash amber, signalling drivers can proceed if the way is clear and safe.
-
Sequence at Pelican Crossings:
- Red Light for Traffic: After a pedestrian presses the button, the traffic light turns red, requiring vehicles to stop.
- Green Man for Pedestrians: Pedestrians get the green signal to cross.
- Flashing Amber for Drivers: Once the green pedestrian signal turns off, the traffic light flashes amber. This indicates drivers may proceed but with caution.
-
Pedestrian Priority: The key here is pedestrian safety:
- Pedestrians who are already crossing during the flashing amber light should be given priority.
- Even though new pedestrians shouldn’t start crossing at this point, any already crossing should be allowed to reach the other side safely.
- Only proceed through the crossing if it’s completely clear of pedestrians.
Additional Tips for Drivers:
- Stay alert for pedestrians near pelican crossings who might be about to press the crossing button.
- Upon seeing a flashing amber light, double-check for any pedestrians still in the process of crossing.
- Use your mirrors to ensure it’s safe to move off, keeping an eye out for other road users and pedestrians who might approach suddenly.
Pulling Away at a Green Traffic Light
Effectively and safely pulling away when a traffic light turns green is a key aspect of driving:
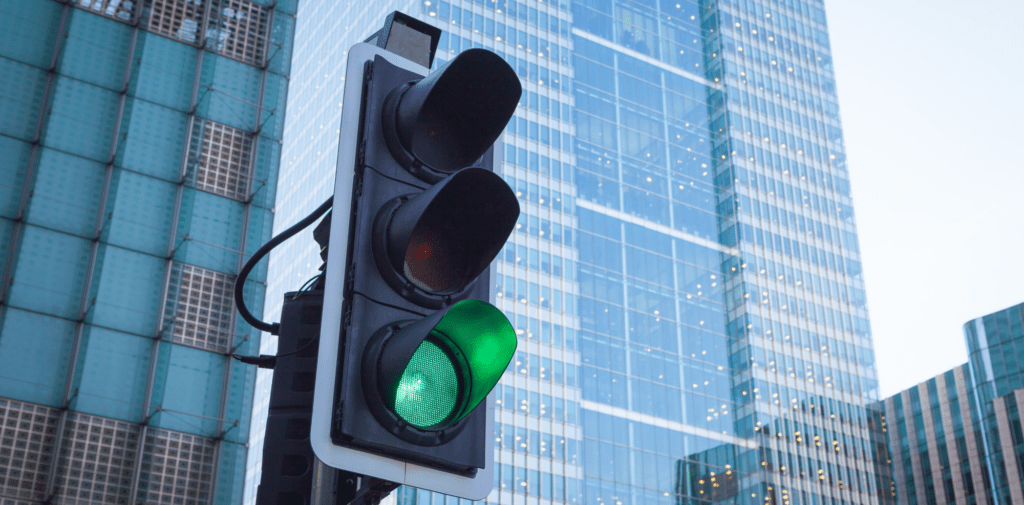

-
Green Means Go: When the traffic lights transition from red and amber to green, it’s your cue to start moving. However, it’s crucial to do this in a controlled and safe manner.
-
Observation and Patience:
- Monitor Traffic: Keep an eye on vehicles ahead. If they haven’t started moving, wait patiently to avoid a collision.
- Pedestrian Awareness: At junctions with pedestrian crossings, ensure no one is still crossing or about to step onto the road.
- Blocked Path: If traffic is congested ahead, it’s better to stay behind the white line until the path is clear.
-
Smooth Departure:
- Handbrake and Clutch: Release your handbrake only when you’re ready to move. Make sure you’ve found your biting point for a smooth pull-off.
- Accelerate Gradually: There’s no need to speed away. A gradual acceleration is safer and better for your vehicle’s longevity.
Key Points for a Pulling off Safely:
- Be vigilant for cyclists and other vulnerable road users who might be near or in the junction.
- Ensure your vehicle is in the correct gear, and you have found the biting point. Then, confidently release your handbrake.
- Proceed with caution and consideration, keeping in mind the flow of traffic and the safety of all road users.
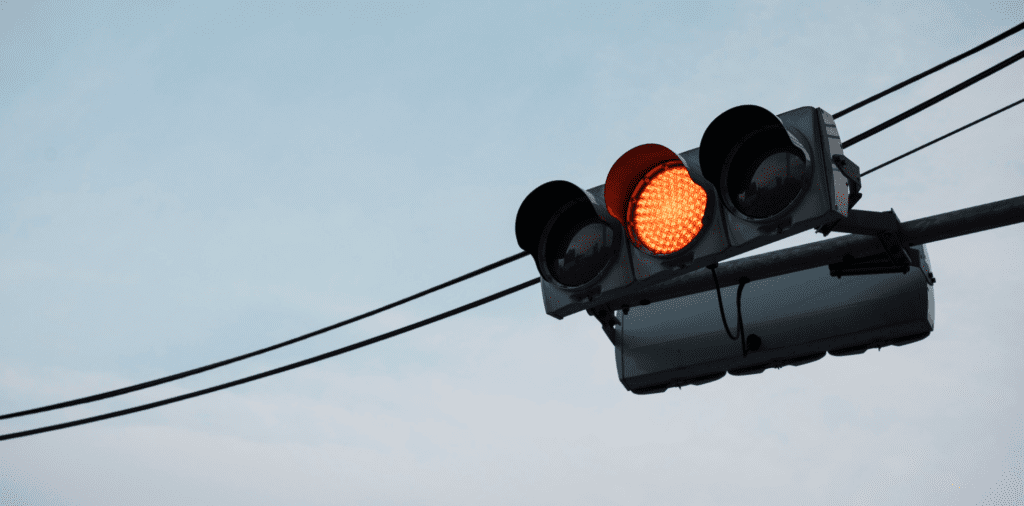
What Should You Do at a Steady Amber Traffic Light?
Navigating through traffic lights is an everyday task for drivers, and understanding the significance of a steady amber light is crucial:

-
Amber Light Means Prepare to Stop: The appearance of a steady amber light typically signals that the lights are about to change to red. The Highway Code mandates that you should stop at an amber light unless:
- You have already crossed the white stop line when the light changes to amber.
- Stopping abruptly would create a risk of an accident, such as being too close to the stop line.
-
Making the Right Decision: Determining whether to stop or proceed during an amber light requires quick judgment. Remember, an amber light is not an invitation to speed up.
-
Anticipation and Awareness: As you approach a traffic light, always be prepared for it to change:
- Mirror Checks: Regularly check your mirrors to be aware of the traffic situation behind you.
- Safe Following Distance: Maintain a safe distance from the vehicle in front. This gives you enough space to safely stop if they brake suddenly.
Key Points for Dealing with Amber Traffic Lights:
- Stop at an amber traffic light unless you’ve passed the stop line or stopping could lead to an accident.
- When driving towards a green light, be ready for the possibility of it changing to amber.
- Constantly stay aware of other road users, including those behind and in front of you, to ensure safe and responsive driving.
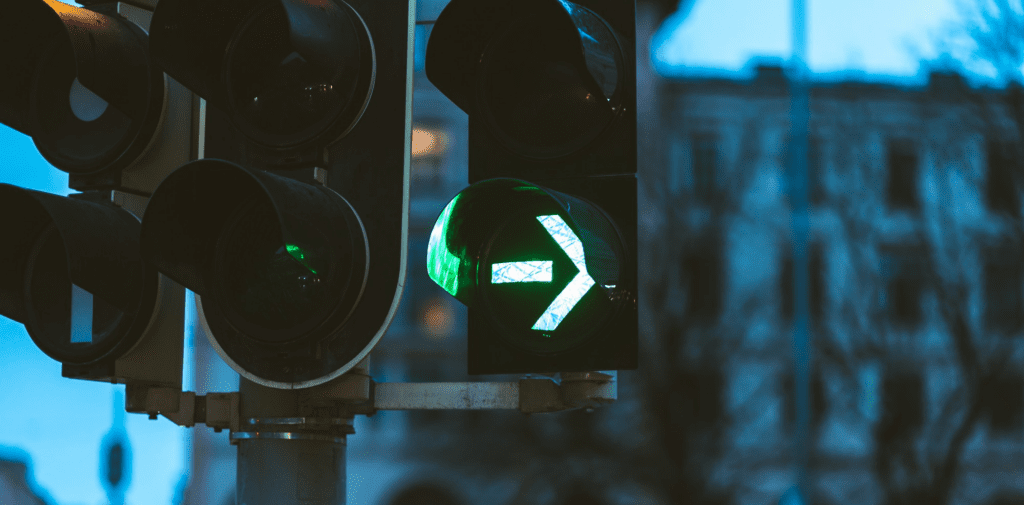
Green Filter Arrow Traffic Light
The green filter arrow at traffic lights is a crucial signal that drivers need to understand and respond to correctly:

-
What is a Green Filter Arrow? This arrow appears at some traffic lights, either in addition to or instead of the standard green light. When lit, it permits movement specifically in the direction the arrow points, regardless of other lights at the junction.
-
Driving Test Expectations: During your driving test, it’s expected that you recognise and appropriately react to filter arrows. Failing to follow these signals, particularly if it hinders other drivers, can result in a major fault and consequently, a failed test.
Turning Right at a Filter Arrow
-
Common in Right Turns: Filter arrows are often used at junctions where a right turn is involved. Right turns are inherently riskier because they cross the path of oncoming traffic.
-
Normal Green Light vs. Filter Arrow:
- Green Light: If there’s a standard green light, you may move forward slightly but should only complete your turn when the path is clear. The oncoming traffic has the right of way.
- Filter Arrow: When the green filter arrow is illuminated, it’s safe to proceed with your turn. The arrow indicates that traffic from other directions is stopped by red lights.
-
Vigilance is Key: Always be alert for filter arrows. They can activate before or after the standard green phase. Even with a filter arrow, it’s important to remain vigilant for pedestrians and cyclists who might be crossing.
Key Points to Remember:
- Always be on the lookout for filter arrows at traffic lights, as they can significantly impact your driving decisions.
- Follow the direction of the filter arrow, understanding that it takes precedence over other light signals at the junction.
Where Do You Stop at a Traffic Light?
Understanding the Stop Line
The stop line is a solid white line marked on the road surface at traffic lights. Its primary function is to indicate where vehicles must come to a halt when the traffic light shows a red or amber light.
Stopping at the stop line ensures that you do not block pedestrian crossings or the intersection itself, thus maintaining safety and smooth traffic flow.
When approaching a traffic light, you should always aim to stop before the stop line. If your vehicle crosses this line when the light changes to red, you could be penalised for a traffic violation.
Additionally, being aware of the stop line helps you avoid obstructing the path for other road users, including cyclists and pedestrians.
Yellow Box Junctions
Yellow box junctions are marked with criss-cross yellow lines and are designed to prevent gridlock at intersections.
These boxes are typically found at busy intersections and indicate areas that must be kept clear at all times, even when the traffic light is green.
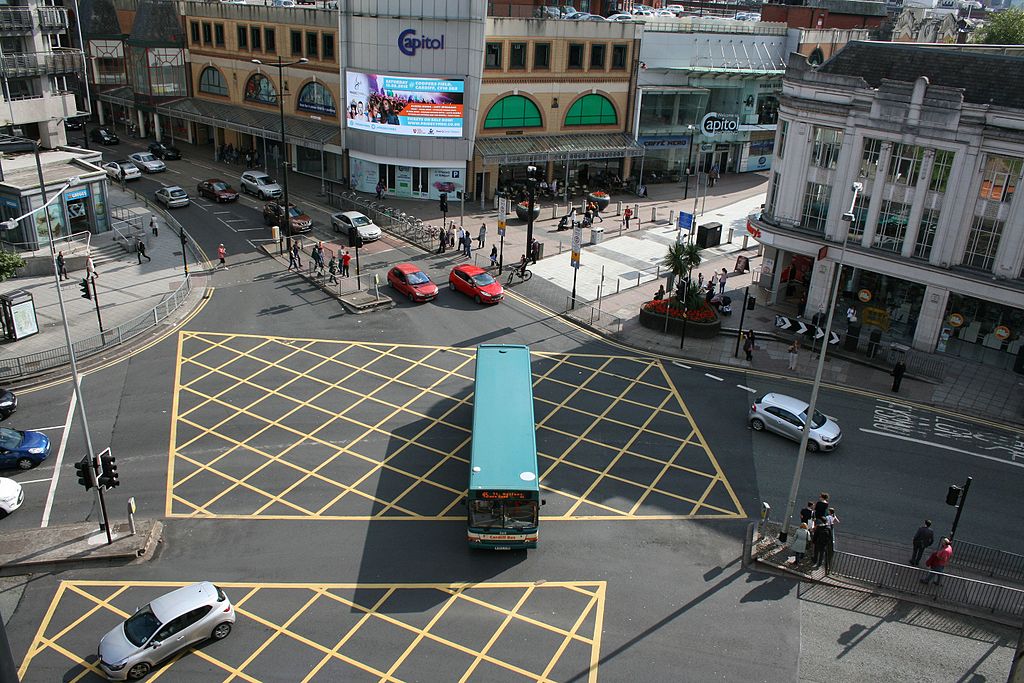

When approaching a yellow box junction, you should only enter the box if your exit is clear and you can cross without stopping.
This rule helps prevent vehicles from being stranded in the middle of the intersection, thereby reducing congestion and improving traffic flow.
If the light turns red while you are in the box, you must still complete your crossing, but you should avoid entering the box unless your way ahead is unobstructed.
Pedestrian Crossings
Pedestrian crossings are essential features at intersections controlled by traffic lights. These crossings are marked with zebra stripes and sometimes accompanied by pedestrian signals.
When a traffic light changes to red, vehicles must stop before the stop line to allow pedestrians to cross safely.

In addition to traditional zebra crossings, you may encounter puffin, pelican, and toucan crossings, each with its specific signal system.
Regardless of the type, the key rule remains: stop at the stop line and ensure the crossing is clear of pedestrians before proceeding.
Advanced Stop Lines for Cyclists
Advanced stop lines are additional markings found at some intersections, specifically designed to accommodate cyclists.
These lines create a designated space ahead of motor vehicles where cyclists can wait for the light to change.
This positioning allows cyclists to be more visible to drivers and gives them a head start when the light turns green, enhancing their safety.
When approaching an intersection with an advanced stop line, motorists must stop at the first line they encounter, even if there is a second line further ahead for cyclists.
This practice ensures that cyclists have the necessary space to position themselves safely at the front of the queue.
Situations with No Clear Stop Line
In some situations, there may be no clear stop line at a traffic light. This scenario can occur due to faded road markings, roadworks, or temporary traffic signals.
In such cases, the general rule is to stop before the traffic light itself or where you have a clear view of the intersection and can safely wait without obstructing other road users.
If you are unsure, it is always safer to stop slightly earlier rather than risk crossing into the intersection inadvertently.
Ensuring that you do not block pedestrian paths or the junction helps maintain order and safety, even in the absence of clear markings.
Are There Any Driving Test Traffic Light Tips?
Observing the Lights Early
When preparing for your driving test, observing the lights early is a critical skill. As you approach an intersection, keep an eye on the traffic lights from a distance.
This early observation helps you anticipate changes and react appropriately. Watching the lights early allows you to make smoother and safer decisions, such as gradually slowing down or preparing to stop.
Preparing to Stop
A key aspect of handling traffic lights during your driving test is preparing to stop. When you see an amber light, you should begin to slow down and prepare to stop unless it is unsafe to do so.
Practising this habit ensures that you can bring your vehicle to a smooth and controlled stop at the stop line, avoiding sudden braking that could be dangerous or unsettling for other road users.
Smooth Acceleration on Green
When the traffic light turns green, it is essential to proceed with smooth acceleration. This means gently pressing the accelerator to move forward without jerking or sudden movements.
Smooth acceleration helps maintain control of your vehicle and ensures a comfortable ride for passengers. It also demonstrates to the examiner that you can handle the car with finesse and awareness of your surroundings.
Dealing with Filter Lights
Filter lights can be a bit tricky during a driving test. These lights indicate a specific direction you are allowed to travel, often shown by a green arrow.
When dealing with filter lights, make sure you understand their meaning and follow them accurately. If a green arrow allows you to turn left or right, ensure you only proceed in that direction.
Misinterpreting a filter light can lead to errors and potential safety hazards during your test.
Practising at Different Types of Intersections
To be fully prepared for your driving test, it is beneficial to practise at different types of intersections.
This includes standard traffic light intersections, yellow box junctions, pedestrian crossings, and roundabouts.
Each type presents unique challenges and learning how to navigate them confidently is crucial.
Practising in varied settings helps you build the necessary skills and adaptability to handle whatever situation arises during your driving test.
Frequently asked questions
Traffic lights are designed to regulate the flow of vehicles and pedestrians, ensuring safe and efficient passage through intersections and crossings.
They help prevent accidents and manage traffic flow by assigning the right of way to different streams of traffic.
A red light means stop. You must bring your vehicle to a complete halt before the stop line, pedestrian crossing, or intersection.
Proceeding through a red light is illegal and can result in penalties.
When the amber light is illuminated, you should prepare to stop if it is safe to do so.
If you are too close to the intersection to stop safely, proceed with caution. The amber light serves as a warning that the signal is about to change to red.
A green light means it is safe to proceed through the intersection. However, you should always check that the intersection is clear of other vehicles, pedestrians, and obstructions before moving forward.
Flashing amber lights generally indicate that you should proceed with caution.
These are often used at pedestrian crossings or areas with unusual traffic patterns or hazards. At pedestrian crossings, you must give way to pedestrians before proceeding.
Filter arrows are additional signals that direct traffic in a specific direction. A green filter arrow allows you to proceed in the direction indicated, even if the main light is red. Follow the direction of the arrow while being cautious of other road users.
You should stop at the stop line, a solid white line marked on the road surface before the intersection or pedestrian crossing. Stopping at this line ensures you do not block pedestrian paths or the intersection.
A yellow box junction is an area marked with criss-cross yellow lines to prevent gridlock at intersections.
You should only enter the box if your exit is clear, ensuring you can cross without stopping inside the box.
At a pedestrian crossing with traffic lights, you must stop at the stop line when the light is red.
Wait until the crossing is clear of pedestrians before proceeding when the light turns green.
Advanced stop lines provide a designated space for cyclists to wait at the front of the queue at traffic lights.
Motorists must stop at the first line they encounter, ensuring that cyclists have space to position themselves safely.
Yes, it is illegal to go through a red light. Doing so can result in fines, points on your licence, and potentially more severe penalties if the action causes an accident.
The standard penalty for running a red light includes a fine of £100 and three points on your driving licence.
Repeated offences or more severe cases can result in higher fines and potential disqualification from driving.
Exceptions are rare but may include situations such as being directed by a police officer or moving out of the way for an emergency vehicle. These situations must be justified and proven if challenged.
If you accidentally cross a red light, stay calm and clear the intersection safely.
If caught on camera, consider consulting a legal advisor, especially if you have a valid reason for the accidental crossing.
Attending a driver awareness course may be an alternative to receiving points on your licence.
Key tips include:
- Observing the lights early
- Preparing to stop at amber
- Using smooth acceleration on green
- Correctly responding to filter lights
- Practicing at different types of intersections
These practices help ensure safe and confident navigation through traffic lights during your test.