Ensuring the correct adjustment of your vehicle’s head restraint is a crucial step towards enhancing both safety and comfort while driving.
This comprehensive guide explores the importance of head restraints, how proper adjustment can prevent injuries, and how to assess and correct your current setup.
Understanding the Importance of Proper Head Restraint Adjustment
The Role of Head Restraints in Vehicle Safety
Head restraints are an integral part of a vehicle’s safety features, designed to limit the movement of the head during a collision.
This is especially crucial in rear-end collisions where the risk of whiplash injuries is significant. Properly adjusted head restraints ensure that the head and neck are adequately supported, significantly reducing the likelihood of neck injuries by restricting the backward movement of the head.
How Correctly Adjusted Head Restraints Prevent Injuries
The effectiveness of a head restraint in preventing injuries lies in its positioning relative to the occupant’s head.
A correctly adjusted head restraint will align closely with the back of the head and the top of the ears.
This alignment helps to catch the head more quickly during a collision, reducing the neck’s snapping movement and thereby minimising the risk of soft-tissue injuries to the neck, commonly known as whiplash.
The Difference Between Head Restraints and Headrests
While often used interchangeably, the terms head restraints and headrests signify different functions.
A head restraint is a safety feature designed to limit the rearward movement of the head in a crash, thus protecting the cervical vertebrae.
On the other hand, a headrest is more about comfort, providing a place to rest the head while driving or seated in a vehicle. Understanding this distinction is crucial when adjusting the head restraint for safety rather than comfort alone.
Assessing Your Current Head Restraint Setup
Identifying Incorrect Head Restraint Positions
Many drivers and passengers unknowingly adjust their head restraints to a less than optimal position, increasing their risk of injury in the event of an accident.
An incorrect head restraint position is typically too low or too far back relative to the head, reducing its effectiveness in preventing neck injuries.
The ideal position is where the top of the restraint is at least as high as the top of the head and as close to the back of the head as possible.
Common Misconceptions About Head Restraint Usage
There are several common misconceptions about head restraint usage that can compromise safety. One such misconception is that head restraints should be adjusted for comfort rather than safety, leading many to set them at a lower height or further back than recommended.
Another misconception is that head restraints are only necessary for longer trips when, in fact, most accidents occur close to home, making proper adjustment essential at all times.
The Impact of Incorrect Adjustment on Comfort and Safety
Incorrect adjustment of head restraints affects both comfort and safety. If a head restraint is positioned too low, it can increase the force on the neck during a crash, potentially leading to severe injuries.
Conversely, if it is too high, it may become ineffective in supporting the head properly. Additionally, a poorly adjusted head restraint can lead to discomfort during normal driving, particularly on long journeys, by forcing the neck into an unnatural position.
Step-by-Step Guide to Adjusting Your Head Restraint
When to Adjust Your Head Restraint
Adjust your head restraint whenever you change your seating position, or if someone else who uses a different driving position has driven the car.
It’s also good practice to check the adjustment if you’ve had passengers in the back seat, as their adjustments might differ.
Remember, even small changes in seat adjustment can necessitate a change in the position of the head restraint.
Detailed Steps for Proper Adjustment
Follow these detailed steps to ensure your head restraint is properly adjusted:
- Sit in your normal driving position: Position yourself comfortably and naturally in the seat, ensuring that your back is flush against the seat back.
- Reach for the head restraint: Most head restraints can be adjusted by pulling them up or pushing them down. Some might have a button that needs to be pressed to unlock the adjustment mechanism.
- Align the head restraint: The ideal position for the head restraint is for its top to be level with the top of your head. This maximises the support for your head in the event of a collision.
- Adjust the distance from the head: Ideally, the head restraint should be as close to the back of your head as possible, ideally within 6 centimetres (about 2.5 inches). If your head restraint is adjustable forward and backward, move it to maintain this minimal distance.
- Double-check the alignment: After adjusting, sit back and ensure the head restraint still aligns properly as you naturally sit.
Adjusting for Different Heights and Postures
For different heights and postures, the head restraint needs to accommodate various body sizes and seating preferences effectively:
- Taller individuals will need to raise the head restraint to ensure it aligns with the top of their head.
- Shorter drivers and passengers may find it challenging if the head restraint does not adjust low enough. In such cases, adjusting the seatback angle may help position the head closer to the restraint.
- Different sitting postures can also impact how the head restraint should be adjusted. Those who prefer to recline their seat slightly will need to ensure the head restraint is moved closer to prevent increasing the gap between the head and the restraint.
Special Considerations for Different Types of Vehicles
Adjusting Head Restraints in Cars vs. SUVs
The process of adjusting head restraints can vary slightly between cars and SUVs due to differences in seat design and height.
SUV seats are generally higher, which may require the head restraint to be adjusted higher compared to cars. Always ensure that the restraint is in the optimal position relative to your head, regardless of vehicle type.
Challenges with Older Vehicle Models
Older vehicle models may pose challenges as they might not have adjustable head restraints, or the range of adjustment is limited.
In these cases, consider the safety implications and, if necessary, look into aftermarket solutions that can offer better support. Safety should always be the priority, and upgrading to adjustable restraints could be a worthwhile investment.
Tips for Handling Non-Adjustable Head Restraints
For vehicles with non-adjustable head restraints, here are some tips to enhance safety:
- Check the seat adjustment: Adjusting the seat angle or position may help align your head more closely with the fixed head restraint.
- Use additional supports: If safety regulations and guidelines permit, consider using a specially designed cushion that can reduce the gap between the head and the restraint.
- Consult a professional: If the fixed head restraint is significantly misaligned with your head, consult a vehicle modification expert to explore customization options that can enhance safety.
The Highway Code and Driving Test Requirements
The Highway Code on Head Restraint Safety
The Highway Code underscores the importance of properly adjusted head restraints as a crucial element of vehicle safety.
Read Rule 97 of The Highway Code
It mandates that head restraints be adjusted to correctly fit the morphology of the driver and passengers to minimize the risk of neck injuries in the event of a collision.
Compliance with these guidelines is not only a safety best practice but also a requirement under UK road laws.
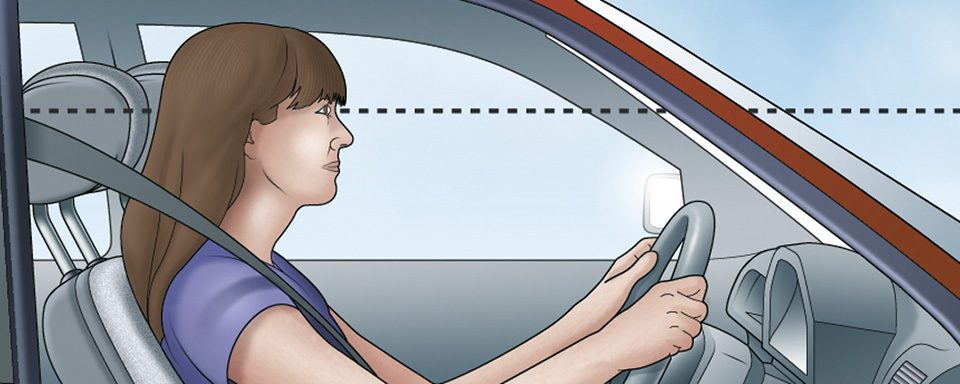
Image source: Open Government Licence v3.0
Show Me, Tell Me: Demonstrating Head Restraint Adjustment
During the UK driving test, the ‘Show Me, Tell Me‘ section requires candidates to demonstrate knowledge and practical skills regarding vehicle safety checks, which include head restraint adjustments.
Candidates might be asked to explain or demonstrate how to adjust the head restraint correctly.

This is an opportunity to show understanding of their functionality and importance, reinforcing the necessity of proper adjustment for safe driving.
Assessing Head Restraint Compliance During the Driving Test
Head restraint compliance is assessed not only in educational settings but also practically during the driving test.
Examiners check whether the head restraint is set to the correct height and position relative to the driver’s head and neck.
This assessment forms part of the overall evaluation of the candidate’s readiness to drive safely and responsibly on public roads.
Maintaining Your Head Restraint
Routine Checks for Head Restraint Integrity
Regular checks are essential to ensure that the head restraints in your vehicle maintain their integrity and functionality.
This involves visually inspecting the restraints for signs of wear or damage, checking that they lock securely into place, and that they can be adjusted smoothly without undue force.
It’s advisable to include head restraint checks as part of your regular vehicle maintenance schedule.
When to Seek Professional Help
It’s important to seek professional help if you notice any issues during your routine checks that you cannot fix yourself, such as a head restraint that fails to stay in place, shows signs of structural weakness, or is damaged.

Professional mechanics can assess whether the head restraint needs to be repaired or replaced, ensuring that it continues to provide the necessary protection.
Upgrading Your Head Restraints for Enhanced Safety
If your vehicle is older or the existing head restraints do not offer adequate adjustability, upgrading your head restraints can significantly enhance safety.
Look for newer models or aftermarket products that comply with current safety standards and are designed to offer better protection against whiplash and other neck injuries.
When selecting new head restraints, ensure they are compatible with your vehicle’s make and model and that they meet any relevant regulatory standards.
Educating Others About Head Restraint Safety
Teaching New Drivers About Head Restraint Adjustment
Educating new drivers about the proper adjustment and importance of head restraints is crucial in fostering a culture of safety from the outset of their driving experience.
Driving instructors and driving schools should include detailed instructions on how to adjust head restraints correctly as part of their curriculum.
This education should emphasize that head restraints are a critical safety feature, not merely a comfort accessory.
New drivers should be taught to adjust the head restraint every time they get into the car, just as they would fasten their seatbelt.
Creating Awareness in Your Community
Creating awareness about head restraint safety can extend beyond the realm of new drivers. Community health organisations, local government, and even car manufacturers can play a part in raising awareness in the broader community.
Organising workshops, safety days, and including messages in driver’s licensing and renewal processes are effective ways to make sure that everyone understands the importance of properly adjusting head restraints.
Information can also be distributed through local media channels, social media, and in collaboration with insurance companies that can incentivize drivers for maintaining proper vehicle safety standards.
The Role of Head Restraints in Overall Vehicle Safety Education
Head restraints play a vital role in overall vehicle safety education. Their importance should be highlighted in various educational formats, including driver’s education courses, in vehicle owner’s manuals, and through public safety campaigns.
Additionally, employers who maintain a fleet of vehicles can include head restraint checks and adjustments as part of their regular safety briefings.
Educating people about how proper adjustment of head restraints can significantly decrease the risk of neck injuries in an accident makes it more likely that individuals will take the time to adjust them properly.
Frequently asked questions
The primary purpose of a head restraint is to prevent neck injuries during a collision by limiting the backward movement of the head, particularly in rear-end accidents.
The top of the head restraint should be as high as the top of your head, or at least level with your eyes.
It should be positioned as close to the back of your head as possible, ideally within 6 centimetres (about 2.5 inches).
No, while they can provide comfort, the main function of head restraints is to enhance safety by protecting against whiplash and other neck injuries in an accident.
Removing head restraints is not recommended as it significantly increases the risk of neck injuries during a crash.
Instead, try adjusting your seat or the head restraint itself to improve comfort.
Most modern vehicles come with adjustable head restraints, but some older models or lower-cost vehicles might have fixed or limited-adjustment head restraints.
It’s good practice to check the adjustment every time you drive, especially if others have used the vehicle, or if the seat position has been changed.
If your head restraint isn’t adjustable and doesn’t fit well, consider using a cushion to reduce the gap between your head and the restraint.
However, ensure this setup does not compromise your driving position or safety.
In many regions, including the UK and EU, there are legal requirements that vehicles must be equipped with head restraints.
These laws also specify standards for their effectiveness in preventing neck injuries.
Children should use head restraints that are appropriate for their height. In some cases, adult head restraints can be adjusted to fit children, but booster seats with dedicated head restraints are often better suited.
Educating others can be effectively done through driving schools, safety workshops, and public awareness campaigns.
It’s also helpful to include information in vehicle manuals and through health and safety programs in workplaces.